All sequence information was downloaded in FASTA format from the FTP site of NCBI. We used a shell script based on wget to retrieve FASTA information of all species for which the genome sequence is available.
The script checks for timestamps of the files on the remote server to skip any FASTA file that is already downloaded. This lets us run the script regularly to fetch any new genome information that has been released.
Only perfect repeats of lengths >= 12nt were considered.
A total of 5356 possible permutations of 1 to 6nt are possible. These are categorized into 501 unique repeat classes based on the cyclical variations of the motif and its reverse complement.
All cyclical variations of the repeat motif are considered to be on the '+' strand whereas those of its reverse complement are considered to be on the '-' strand. In case the repeat motif is a palindrome or a cyclical variation of a palindrome, all the cyclical variations are considered to be on the '+' strand.
This is better explained in the table below:
| Repeat Class | Cyclical Variations ('+' strand) | Reverse Complement ('-' strand) | Number of motifs in class |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACT | ACT, CTA, TAC | AGT, GTA, TAG | 6 |
| ACGT | ACGT, CGTA, GTAC, TACG | ACGT, CGTA, GTAC, TACG | 4 |
| AATTCG | AATTCG, ATTCGA, TTCGAA, TCGAAT, CGAATT, GAATTC | CGAATT, GAATTC, AATTCG, ATTCGA, TTCGAA, TCGAAT | 6 |
Number of species for which data is available
|
Database
Kingdom/Group |
Micro Organism Tandem Repeats Database | UgMicroSatDb | Kazusa Marker Database | Plant Microsatellite DNAs database | Tandem Repeats Database | FishMicroSat | Polymorphic Simple Sequence Repeats Database | MICAS | EuMicroSatDb | MSDB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | 1109 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 85 | 4772 | 0 | 5732 |
| Archaea | 91 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 217 | 0 | 514 |
| Plants | 0 | 80 | 14 | 110 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 74 |
| Fungi | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 191 | ||
| Protozoa | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 72 | ||
| Invertebrates | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 112 | ||
| Vertebrates | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 190 | 0 | 0 | 198 | ||
| Viruses | 1463 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Database Features
|
Database
Kingdom/Group |
Micro Organism Tandem Repeats Database | UgMicroSatDb | Kazusa Marker Database | Plant Microsatellite DNAs database | Tandem Repeats Database | FishMicroSat | Polymorphic Simple Sequence Repeats Database | MICAS | EuMicroSatDb | MSDB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interactive tables with column filters | Yes1 | Yes1 | No4 | Yes5 | Yes | No | No4 | Yes1 | Yes1 | Yes |
| Downstream analysis plots | No | No | No | No | No | Yes6 | No | No | No | Yes |
| Comparison of data from multiple organisms | No2 | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| Taxonomic Grouping | Yes3 | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes3 | No | Yes |
| Data Download | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes |
1 - Does not support dynamic filtering of the results. The filtering parameters should be selected initially
2 - Comparison only across different strains of same species 3 - Grouping only based on the kingdoms 4 - Only a tabular view of the data without dynamic filters 5 - Filtering only based on the type of repeat 6 - Only pie charts available |
As explained earlier, there are 501 unique repeat classes into which all possible kmer combinations of 1 to 6nt motifs are classified. Hence, a repeat class can contain several repeat motifs. For example, AGAT, GATA, ATAG and TAGA are all part of the AGAT repeat class.
Actual repeat is defined as the motif that is present at the beginning of the repeat sequence, as described in the image below.
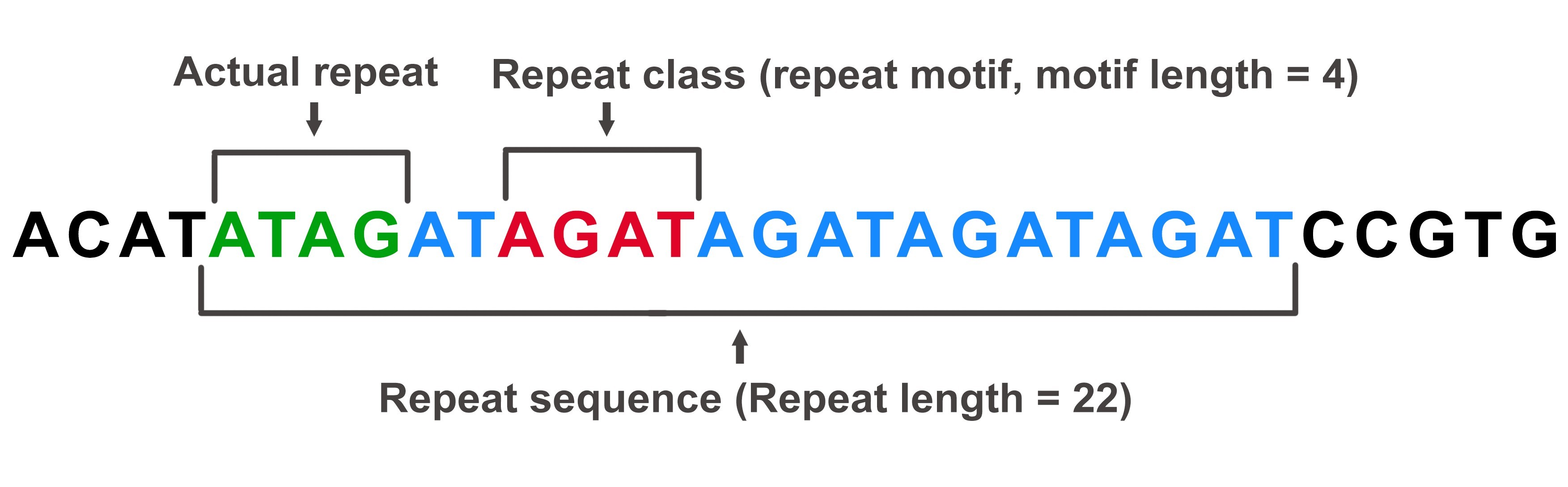
In this example, the actual repeat is ATAG, as determined by the first 4 bases of the entire repeat sequence. However, this repeat falls into the AGAT class.

In this example, the actual repeat is ATAG, as determined by the first 4 bases of the entire repeat sequence. However, this repeat falls into the AGAT class.
We generally update the sequence information every couple of months. Hence, any genome that is released recently may not be available yet on MSDB.
However, if you come across any species for which the sequence information has been available for a while and is still missing in our database, please let us know. We will be happy to include it in our database as quickly as possible.
Currently, no. We are in the process of adding common name annotations for as many species as possible. This feature should roll out soon.